Unlock the Future of Money: Your Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is more than just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force reshaping the financial landscape. From Bitcoin’s inception in 2009 to the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), the crypto space has evolved rapidly, offering unparalleled opportunities and challenges. This comprehensive guide will take you through the fundamentals of cryptocurrency, its underlying technology, and its diverse applications, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this digital frontier.
1. What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of money designed to function as a medium of exchange. Unlike traditional currencies controlled by central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks that leverage blockchain technology. This ensures transparency, security, and immutability.
Key Features:
- Decentralization: Cryptocurrencies operate on peer-to-peer networks, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Security: Advanced cryptographic techniques protect transactions and user data.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, promoting accountability.
- Global Accessibility: Cryptocurrencies enable borderless transactions, empowering individuals worldwide.
2. The Evolution of Cryptocurrency
The journey of cryptocurrency began with Bitcoin, the first decentralized digital currency introduced by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Over the years, numerous cryptocurrencies have emerged, each serving unique purposes.
Milestones in Cryptocurrency History:
- 2009: Bitcoin’s launch, marking the advent of decentralized digital currency.
- 2013: Introduction of Ethereum, enabling smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- 2017: The ICO (Initial Coin Offering) boom, raising billions for blockchain projects.
- 2020: The rise of DeFi, transforming traditional financial services like lending and trading.
- 2021: NFT explosion, revolutionizing digital ownership in art, gaming, and entertainment.
3. How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
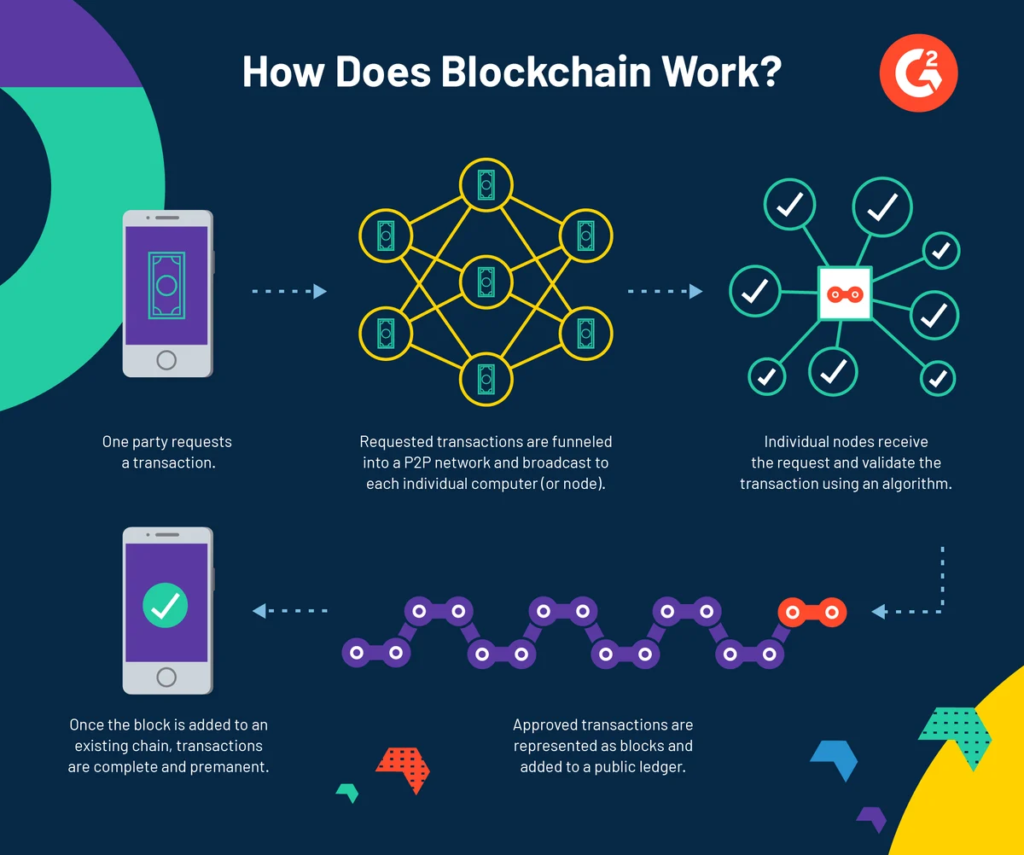
At its core, cryptocurrency relies on blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network. Each transaction is grouped into a “block” and added to a “chain” in chronological order.
Key Components:
- Blockchain: A decentralized, immutable ledger.
- Nodes: Independent computers that validate transactions.
- Mining/Validation: The process of verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain.
- Wallets: Tools for storing and managing digital assets.
4. Types of Cryptocurrencies

The cryptocurrency market comprises thousands of digital assets, each with unique features and use cases.
1. Bitcoin (BTC):
Often referred to as “digital gold,” Bitcoin serves as a store of value and a medium of exchange. Its capped supply of 21 million coins ensures scarcity, driving its value.
2. Ethereum (ETH):
Ethereum extends beyond a digital currency, offering a platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts. It powers DeFi projects, NFTs, and more.
3. Stablecoins (e.g., USDT, USDC):
Stablecoins are pegged to traditional assets like the US dollar, providing stability in the volatile crypto market.
4. Altcoins (e.g., Solana, Cardano):
These are alternatives to Bitcoin, often focusing on scalability, efficiency, and specific use cases.
5. Benefits of Cryptocurrency

1. Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrencies empower the unbanked population by providing access to financial services without the need for traditional banking infrastructure.
2. Lower Transaction Costs
Crypto transactions often incur lower fees compared to traditional banking or payment systems, especially for cross-border payments.
3. Decentralization and Autonomy
Users maintain control over their funds, reducing dependency on centralized institutions.
4. Investment Opportunities
The crypto market offers lucrative investment options, from trading and staking to yield farming and NFTs.
5. Enhanced Security
Cryptographic security and blockchain transparency mitigate fraud and unauthorized access.
6. Risks and Challenges

Despite its advantages, cryptocurrency carries inherent risks.
1. Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile, leading to significant price swings within short periods.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments worldwide are still formulating regulations, creating uncertainty for investors and businesses.
3. Security Concerns
While blockchain technology is secure, crypto exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacking.
4. Scams and Fraud
The crypto space has witnessed numerous scams, including Ponzi schemes and fraudulent ICOs.
5. Environmental Impact
The energy-intensive process of mining certain cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, raises environmental concerns.
7. Applications of Cryptocurrency

The versatility of cryptocurrencies extends beyond financial transactions, offering innovative solutions across various industries.
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms replicate traditional financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. Popular DeFi projects include Aave, Uniswap, and Compound.
2. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs represent unique digital assets, enabling ownership of digital art, collectibles, and in-game items. Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible have popularized NFT trading.
3. Cross-Border Payments
Cryptocurrencies facilitate fast, low-cost international transfers, reducing reliance on traditional remittance services.
4. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains, ensuring product authenticity and ethical sourcing.
5. Gaming and Metaverse
Crypto is integral to the gaming industry, powering play-to-earn models and virtual economies in the metaverse.
8. How to Get Started with Cryptocurrency

If you’re new to cryptocurrency, follow these steps to begin your journey:
1. Educate Yourself
Understand the basics of blockchain, cryptocurrency, and market trends. Resources like online courses, forums, and whitepapers are invaluable.
2. Choose a Reliable Wallet
Select a cryptocurrency wallet to store your digital assets securely. Options include:
- Hardware Wallets (e.g., Ledger, Trezor): Offline storage for enhanced security.
- Software Wallets (e.g., MetaMask, Trust Wallet): Convenient for daily transactions.
3. Select a Cryptocurrency Exchange
Exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken enable buying, selling, and trading of cryptocurrencies. Compare fees, security features, and supported assets before choosing.
4. Start Small
Invest a small amount initially to familiarize yourself with market dynamics and trading platforms.
5. Secure Your Investments
Use two-factor authentication (2FA), regularly update passwords, and avoid sharing private keys to enhance security.
9. Future of Cryptocurrency

The future of cryptocurrency is promising, with innovations poised to disrupt traditional systems further.
1. Mass Adoption
As regulatory clarity improves, mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies for payments, investments, and beyond is likely to increase.
2. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Governments worldwide are exploring CBDCs, combining the benefits of cryptocurrencies with state-backed security.
3. Interoperability
Advancements in blockchain technology aim to enhance interoperability between different networks, improving efficiency and user experience.
4. Sustainability Initiatives
Efforts to develop eco-friendly consensus mechanisms, such as Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake (PoS), will address environmental concerns.
5. Integration with Emerging Technologies
The convergence of blockchain with artificial intelligence, IoT, and quantum computing could unlock new possibilities.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency is not just a fleeting trend but a fundamental shift in how we perceive and interact with money, assets, and technology. Whether you’re an investor, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the digital economy, understanding the intricacies of cryptocurrency is your first step toward unlocking its full potential. Embrace this revolutionary technology, and be part of the future of money.




